Team Name
Majestic
Timeline
Summer 2023 – Fall 2023
Students
- Efrain Morales Loya
- Michael Allen
- Chau Ngyuen
- Jaime Barajas
- Khoi Tran
Sponsor
Erica Hinojosa
Abstract
The RFID Smart Stethoscope is a tool designed to help train nursing students at the UTA smart hospital. The Stethoscope allows for a nursing student using it to scan a simulated patient wearing an RFID shirt and hear the desired sounds that would normally not be able to be detected through the use of a normal stethoscope on a healthy sim patient. It also allows the smart hospital to program different situations for the stethoscope to simulate to allow for training in the detection of a wide variety of ailments.
Background
At the university’s smart hospital, they bring in paid actors called standardized patients who act like they have ailments and diseases to help train the nursing students to identify and treat those ailments. The issue that the university is having with these patients is that they are healthy so their internal body sounds are those of a healthy individual, and so the university cannot train the nurses to listen for unhealthy sounds within the patient’s body. To help train their nursing students to use a stethoscope to listen for different auscultation sounds within the heart, lungs, and bowels of the healthy standardized patients this project will use a set of chips that the standardized patient can wear. When these chips are scanned it will play the audio corresponding to the part of the body that was just scanned. This allows for the nursing students to hear sounds that the standardized patients body would normally not be making. To allow for a wide variety of different simulations that the smart hospital might want to run these chips must be able to be reprogrammed easily to allow for any ailment that the smart hospital wishes to train the students for that day.
Project Requirements
- The product shall reproduce a variety of clear and authentic auscultation sounds such as normal, wheezes, rhonchi, stridor, etc.
- The product shall be fully compatible with Raspberry Pi Zero, allowing proper interfacing and communication protocols.
- The product shall integrate into a wearable design that can be easily embedded in a shirt or other garment.
- The product shall provide real-time feedback to simulate actual patient conditions, including synchronization between RFID chip sounds and the position of the stethoscope.
- The product shall be designed for efficient power consumption, enabling extended battery life.
- The product shall include an intuitive user interface to allow customization of auscultation sounds and scenarios.
- The product shall demonstrate robustness and reliability to withstand regular usage in a medical training environment
- The product shall comply with relevant medical and technological standards, including considerations for safety and legality.
- The product shall be scalable and expandable to support additional functionalities or integration with other medical simulators in the future
- The product shall be accessible and cost-effective, supporting implementation and maintenance without sacrificing quality.
System Overview
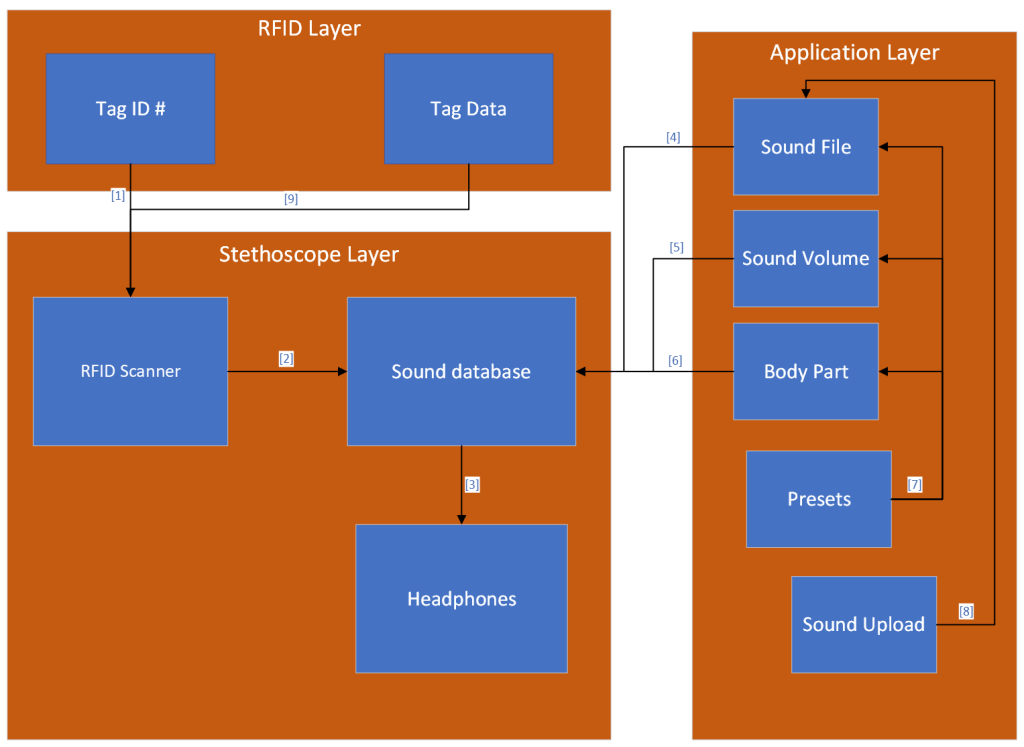
This system will have a shirt that contains many RFID or NFC chips within it. When these chips are scanned, they will send a unique ID number to a small on-board computer that tells the computer what part of the body that tag is from. The computer will use that ID number to look at a table of audio files that each correspond to a specific part of the patient’s body. Then after finding the correct audio file to play based on the RFID or NFC chip’s ID number it will play that sound to the headphones that the user of the stethoscope is wearing. The table inside of the on-board computer will be populated by an external application and then written to the system. The application will allow the user to upload new audio files and then select which parts of the body play which audio sounds.
Results
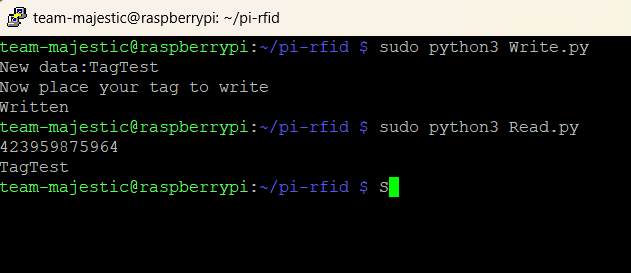
Basic reading to and writing from the RFID tags using the raspberry pi 0.
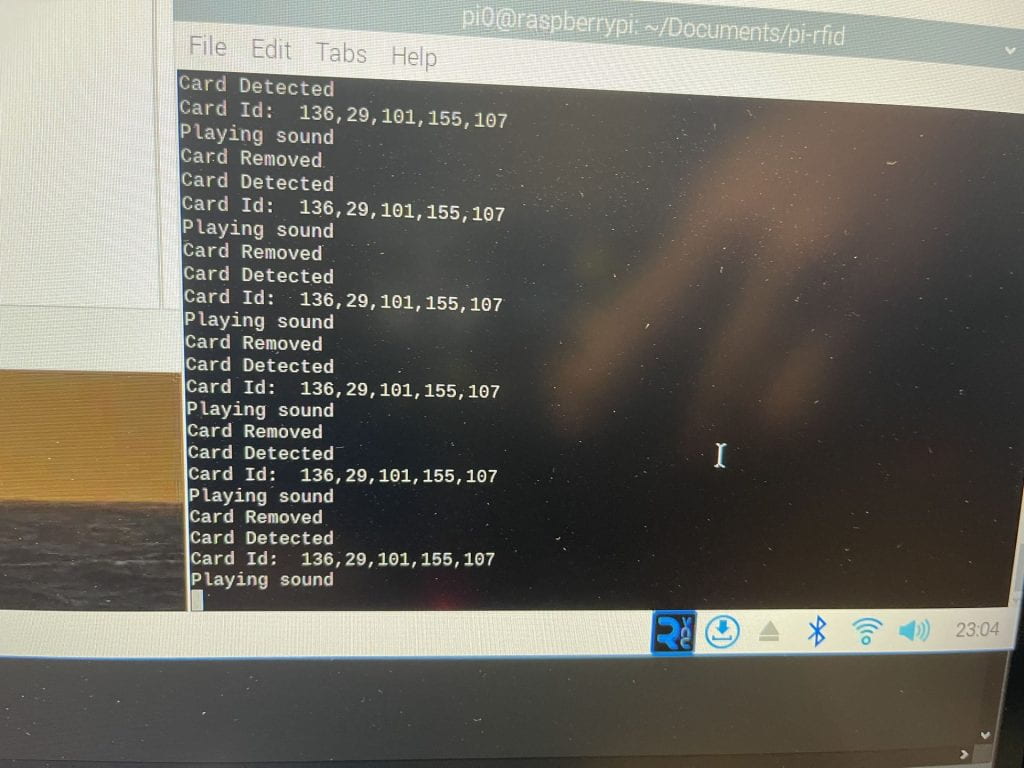
Read to audio playback functionality working when the RFID reader scans the tags on the shirt.
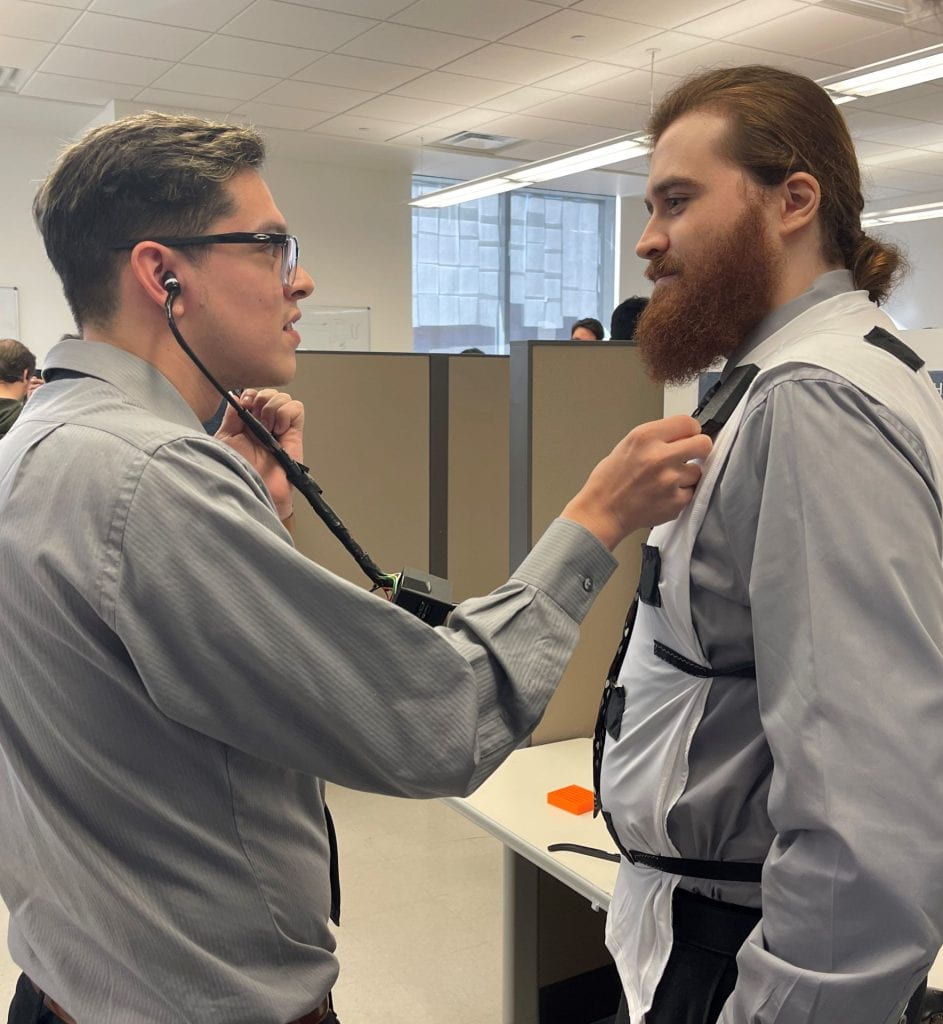

Sethoscope in use listening to sounds on the shirt.
Application demo video.
Future Work
- The product shall develop a broader library of auscultation sounds, including specialized medical conditions.
- The product shall improve the wearable design to enhance comfort and appearance for prolonged usage.
- The product shall integrate with other simulation tools like visual patient monitors or virtual reality setups for comprehensive training.
- The product shall focus on energy efficiency and sustainability,considering advanced power management and environmentally friendly practices.
Project Files
Project Charter (link)
System Requirements Specification (link)
Architectural Design Specification (link)
Detailed Design Specification (link)
Poster (link)
References
- “Pisugar 3: Battery for raspberry pi zero,” 2021, hardware component.
- R. P. Foundation, “Raspberry pi zero,” 2015, hardware component.
- RASPIAUDIO, “Audio dac hat sound card (audio+v2) for raspberry pi4 all models pi zero / pi3 / pi3b / pi3b+ / pi2,” 2019, better Quality Than USB. Hardware component.
- “Rfid laundry tags 13.56 mhz hf,” 2019, designed to be imbedded or attached to bed linens, towels,and primary medical scrubs or uniforms. PPS + epoxy design. Available with both ISO 15693 and14443 NFC memory chips.
- Stemedu, “Rc522 rfid reader writer module rf ic card sensor with s50 white card + writable keyring for arduino for raspberry pi nano nodemcu (pack of 2sets),” 2018, hardware component.